Cemented carbide nozzle is a precision spraying component made with tungsten carbide powder (WC powder) as the hard phase and cobalt or nickel as the binder phase through powder metallurgy process. It exhibits excellent comprehensive performance in high-temperature, high-speed erosion, and strong corrosion environments, making it currently the most widely used high-end material in the industrial nozzle field. For any cemented carbide nozzle products, please contact CTIA GROUP LTD: [email protected], 0592-5129595. For more information on cemented carbide, please visit: http://www.tungsten-carbide.com.cn/index.html
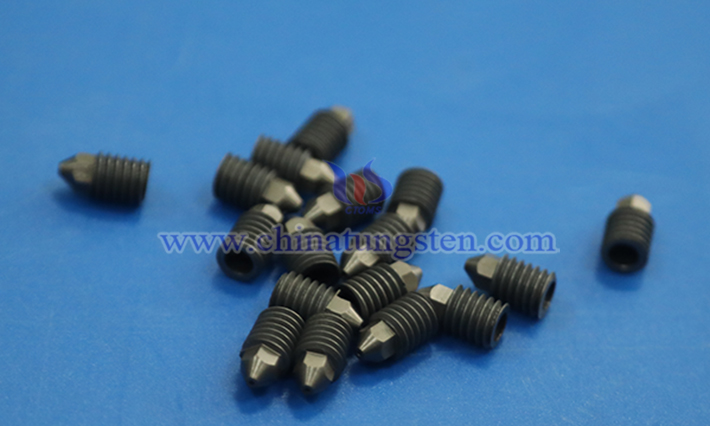

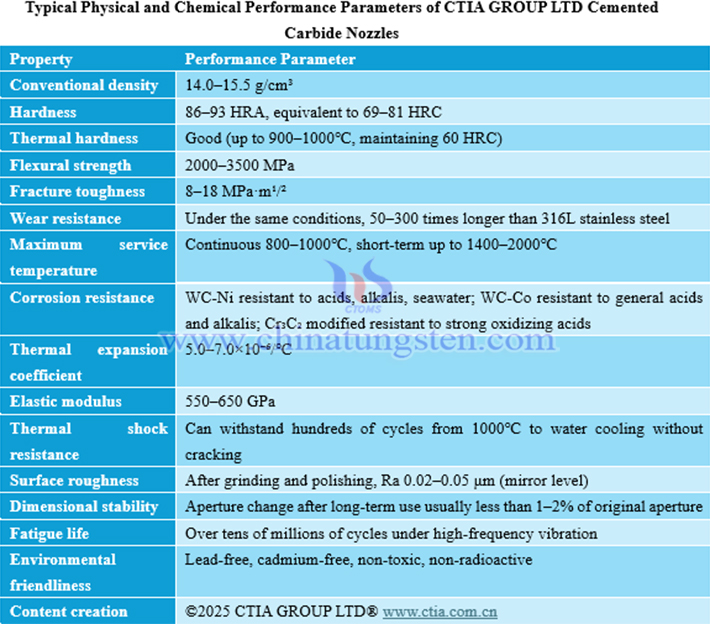
1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Cemented Carbide Nozzles
Cemented carbide nozzles have excellent comprehensive performance, combining outstanding mechanical and environmental adaptation characteristics. Their hardness and wear resistance are prominent, allowing long-term structural stability under complex conditions and effectively extending service life; thermal hardness and thermal shock resistance perform well, capable of withstanding large temperature changes and suitable for high-temperature operation scenarios. They also have reliable corrosion resistance, adaptable to a variety of complex media environments, with strong dimensional stability and minimal performance degradation after long-term use. In addition, the material is environmentally friendly and non-toxic, containing no harmful components, meeting green application requirements and having a wide range of applications.
2. Classification of Cemented Carbide Nozzles
The classification system of cemented carbide nozzles covers eight key dimensions: binder phase, WC grain size, binder phase content, second phase addition, structural form, surface treatment, connection method, and precision grade. Each dimension has multiple typical categories, clarifying performance characteristics of different specifications, such as cobalt-based binder phase nozzles having high cost-performance, submicron grain size products having excellent wear resistance, and also matching adaptation scenarios, such as Venturi structure suitable for sandblasting, HVOF and other supersonic applications, ultra-precision grade meeting high requirements for water cutting, semiconductor wet etching, etc.

3. Production Methods of Cemented Carbide Nozzles
The production methods of cemented carbide nozzles are mainly based on powder metallurgy process, with steps including (1) raw material preparation, (2) forming, (3) sintering, (4) finishing, and (5) inspection.
The raw material preparation stage is to weigh tungsten carbide powder and cobalt/nickel binder phase powder in preset proportions, wet-mill and mix them in a ball mill with organic solvent as medium until tungsten carbide particles are uniformly coated, forming stable composite powder, then spray-dry to produce granular powder with good flowability suitable for subsequent forming.
The forming stage is the key step to convert powder into near-net-shape blanks. Common methods include cold isostatic pressing and injection molding. Cold isostatic pressing uses liquid medium to apply uniform pressure, densifying the powder in a flexible mold to form blanks with uniform density distribution; injection molding first mixes the powder with organic binder into flowable slurry, injects it into precision molds for curing and demolding.
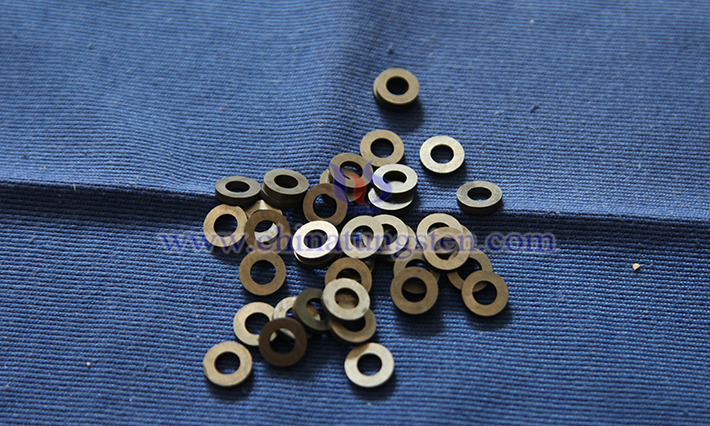

Sintering is the core process, through high-temperature treatment under vacuum or hydrogen protection atmosphere, melting the binder phase to wet tungsten carbide particles and achieve liquid-phase densification. The process is divided into pre-sintering and main sintering: pre-sintering slowly removes organics to avoid blank cracking; main sintering controls temperature gradient to promote particle rearrangement and pore closure, forming cemented carbide body with near-theoretical density. After sintering, blanks need slow cooling to release internal stress.
The finishing stage performs precision grinding and polishing on sintered bodies. Using diamond tools on CNC machines to process flow channels, throats, and outer shapes to achieve mirror-like inner surfaces. Surface treatment can include boronizing or coating with diamond-like carbon film to further enhance corrosion resistance and friction reduction performance.
Final inspection includes dimensional measurement, hardness testing, and pressure testing to ensure each nozzle meets industrial standards.
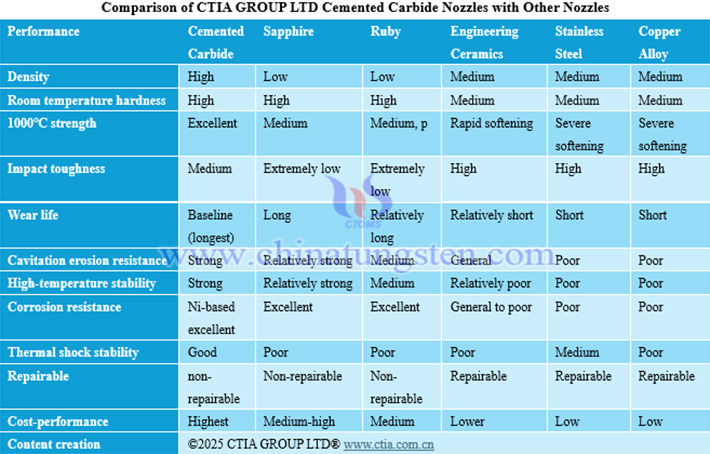
4. Comparison of Cemented Carbide Nozzles with Other Nozzles
Compared with sapphire, ruby, engineering ceramics, stainless steel, and copper alloys, nozzles made of cemented carbide have superior comprehensive performance, better in density, room temperature hardness, high-temperature strength retention, wear resistance, cavitation erosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and cost-performance, applicable to numerous fields, but with the disadvantage of being almost non-repairable. Sapphire and ruby have outstanding hardness and corrosion resistance but low impact toughness and non-repairable, engineering ceramics are repairable but weaker in high-temperature performance, stainless steel and copper alloys are convenient for processing and maintenance but have shortcomings in core performance such as wear resistance and high-temperature resistance, with limited application scenarios.
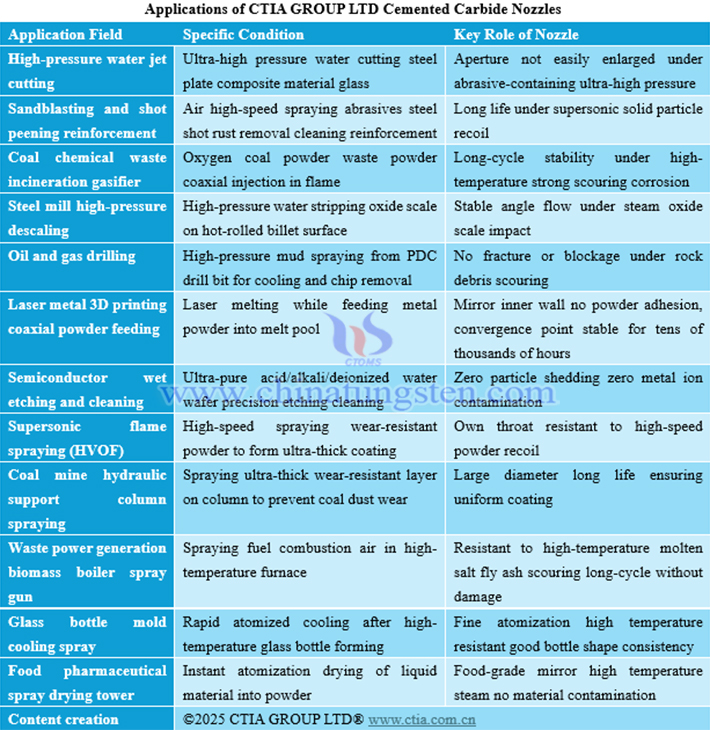
5. Applications of Cemented Carbide Nozzles
Applications of cemented carbide nozzles cover core conditions in multiple industries, including high-pressure water jet cutting, coal chemical gasification, semiconductor cleaning, 3D printing powder feeding, etc. Their key advantages are embodied in extreme environment adaptability: stable aperture under ultra-high pressure, long life under supersonic particle scouring, continuous service under high-temperature corrosion conditions, and possessing characteristics such as environmental friendliness, anti-adhesion, stable flow angle, etc.